Using AutoFilterer with ABP
This article is about filtering data automatically without writing any LINQ via using AutoFilterer.
AutoFilterer is a mini filtering framework library for dotnet. The main purpose of the library is to generate LINQ expressions for Entities over DTOs automatically. Creating queries without writing any expression code is the most powerful feature that is provided. The first aim of AutoFilterer is to be compatible with Open API 3.0 Specifications, unlike oData & GraphQL.
Disclaimer: AutoFilterer is the one of my personal projects. It's not supported by ABP Framework or ABP Team officially. This article can be shown as self-promotion, so I needed to explain that.
Initializing a New Project
If you are familiar with application development with ABP Framework, you can skip to the next step "Designing the Application.Contracts Layer".
- Create a new project:
(I prefer mongodb as database provider to get rid of Ef migrations. You can go with Ef on your own.)
abp new Acme.BookStore -t app -d mongodb
- Create an entity named Book
using System;
using Volo.Abp.Domain.Entities.Auditing;
namespace Acme.BookStore.Books;
public class Book : FullAuditedAggregateRoot<Guid>
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Language { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; }
public string Author { get; set; }
public int TotalPage { get; set; }
public int Year { get; set; }
public string Link { get; set; }
}
- Add following property to BookStoreMongoDbContext
public IMongoCollection<Book> Books { get; set; }
- Create a DataSeedContributor
- Add this initial-books.json file to
Acme.BookStore.Domain/Books/path and make build action as Embedded Resource.
- Add this initial-books.json file to
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Volo.Abp.Data;
using Volo.Abp.DependencyInjection;
using Volo.Abp.Domain.Repositories;
namespace Acme.BookStore.Books;
public class BookstoreDataSeederContributor : IDataSeedContributor, ITransientDependency
{
protected readonly IRepository<Book, Guid> _repository;
public BookstoreDataSeederContributor(IRepository<Book, Guid> repository)
{
_repository = repository;
}
public async Task SeedAsync(DataSeedContext context)
{
if (!await _repository.AnyAsync())
{
await _repository.InsertManyAsync(GetInitialBooks());
}
}
private Book[] GetInitialBooks()
{
var json = GetEmbeddedResourceAsText("Acme.Bookstore.Books.initial-books.json");
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<Book[]>(json);
}
private string GetEmbeddedResourceAsText(string nameWithNamespace)
{
using var stream = GetType().Assembly.GetManifestResourceStream(nameWithNamespace);
return Encoding.UTF8.GetString(stream.GetAllBytes());
}
}
- Run the DbMigrator and database with existing data is ready!
Designing the Application.Contracts Layer
In this section, We'll implement AutoFilterer package and use it for only filtering data. We'll leave Sorting and Paging to ABP Framework, because it already does it well and works with more than one UI compatible.
- Add
AutoFiltererpackage to your Application.Contracts project.
dotnet add package AutoFilterer
Let's start coding with creating DTOs.
- BookDto
using System; using Volo.Abp.Application.Dtos; namespace Acme.BookStore.Books; [Serializable] public class BookDto : AuditedEntityDto<Guid> { public string Title { get; set; } public string Language { get; set; } public string Country { get; set; } public string Author { get; set; } public int TotalPage { get; set; } public int Year { get; set; } public string Link { get; set; } }- BookGetListInput
using AutoFilterer.Attributes; using AutoFilterer.Enums; using AutoFilterer.Types; using System; using Volo.Abp.Application.Dtos; namespace Acme.BookStore.Books; [Serializable] // We'll leave Paging and Sorting to ABP, we'll use only filtering feature of AutoFilterer. // So using FilterBase as a base class is enough. public class BookGetListInput : FilterBase, IPagedAndSortedResultRequest { // Configure 'Filter' property for built-in search boxes. [CompareTo( nameof(BookDto.Title), nameof(BookDto.Language), nameof(BookDto.Author), nameof(BookDto.Country) )] [StringFilterOptions(StringFilterOption.Contains)] public string Filter { get; set; } // IPagedAndSortedResultRequest implementation below. public int SkipCount { get; set; } public int MaxResultCount { get; set; } public string Sorting { get; set; } }- IBookAppService
using System; using Volo.Abp.Application.Services; namespace Acme.BookStore.Books; public interface IBookAppService : ICrudAppService<BookDto, Guid, BookGetListInput> { }
Implementing Application Layer
I prefer using CrudAppService to skip unrelated CRUD operations.
- Create BookAppService and apply AutoFilterer filtering to queryable via overriding CreateFilteredQueryAsync.
using AutoFilterer.Extensions;
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Volo.Abp.Application.Services;
using Volo.Abp.Domain.Repositories;
namespace Acme.BookStore.Books;
public class BookAppService : CrudAppService<Book, BookDto, Guid, BookGetListInput>
{
public BookAppService(IRepository<Book, Guid> repository) : base(repository)
{
}
protected override async Task<IQueryable<Book>> CreateFilteredQueryAsync(BookGetListInput input)
{
return (await base.CreateFilteredQueryAsync(input))
.ApplyFilter(input);
}
}
- Add following mapping in BookStoreApplicationAutoMapperProfile
CreateMap<Book, BookDto>().ReverseMap();
Displaying on UI
Let's start with creating a page to show data list and filter it with a textbox.
- Create
Books/Index.cshtml/Books/Index.cshtml.cs
namespace Acme.BookStore.Web.Pages.Books;
public class IndexModel : BookStorePageModel
{
}
@page
@using Acme.BookStore.Localization
@using Acme.BookStore.Web.Pages.Books
@using Microsoft.Extensions.Localization
@model IndexModel
@inject IStringLocalizer<BookStoreResource> L
<h2>Books</h2>
@section scripts
{
<abp-script src="/Pages/Books/index.js" />
}
<abp-card>
<abp-card-header>
<h2>@L["Books"]</h2>
</abp-card-header>
<abp-card-body>
<abp-table striped-rows="true" id="BooksTable"></abp-table>
</abp-card-body>
</abp-card>
- Create index.js in the same folder
$(function () {
var l = abp.localization.getResource('BookStore');
var dataTable = $('#BooksTable').DataTable(
abp.libs.datatables.normalizeConfiguration({
serverSide: true,
paging: true,
order: [[1, "asc"]],
searching: true,
scrollX: true,
ajax: abp.libs.datatables.createAjax(acme.bookStore.books.book.getList),
columnDefs: [
{
title: l('Title'),
data: "title"
},
{
title: l('Language'),
data: "language",
},
{
title: l('Country'),
data: "country",
},
{
title: l('Author'),
data: "author"
},
{
title: l('TotalPage'),
data: "totalPage",
render: function (data) {
return data + ' pages'
}
},
{
title: l('Year'),
data: "year"
},
{
title: l('Link'),
data: "link",
render: function (data) {
return '<a href="' + data + '" target="_blank">Link</a>';
}
},
]
})
);
});
- Run the project and see how it's working!
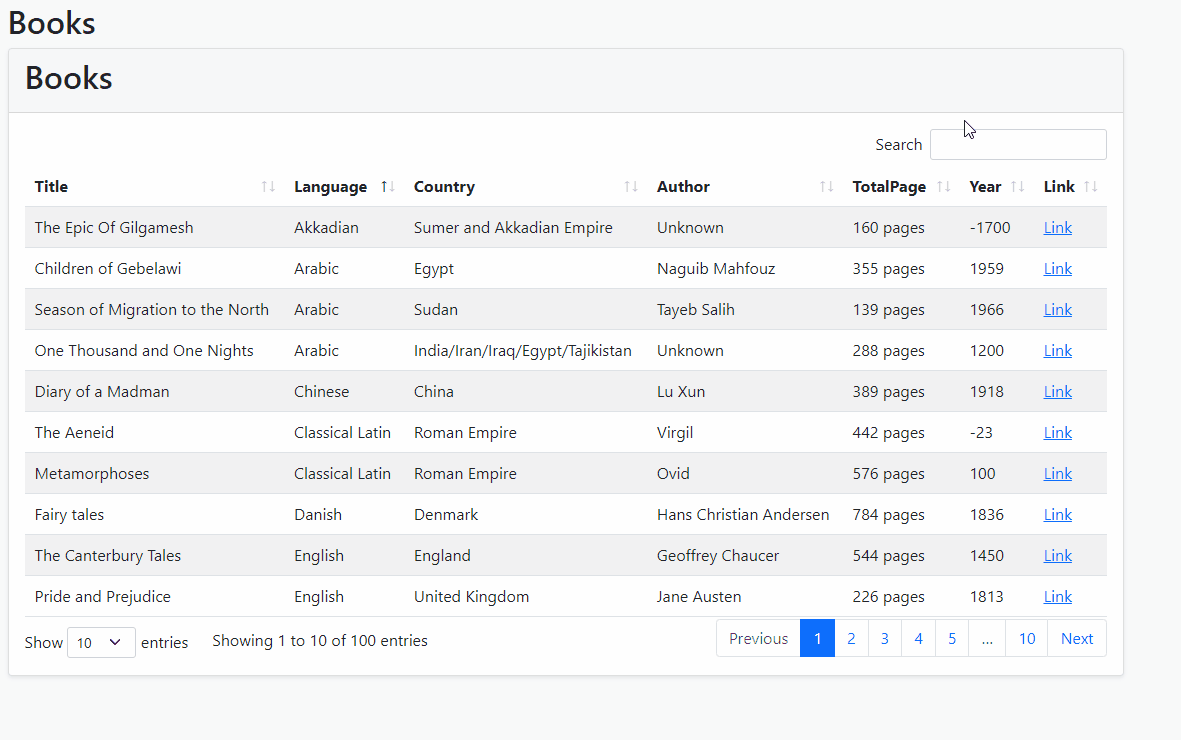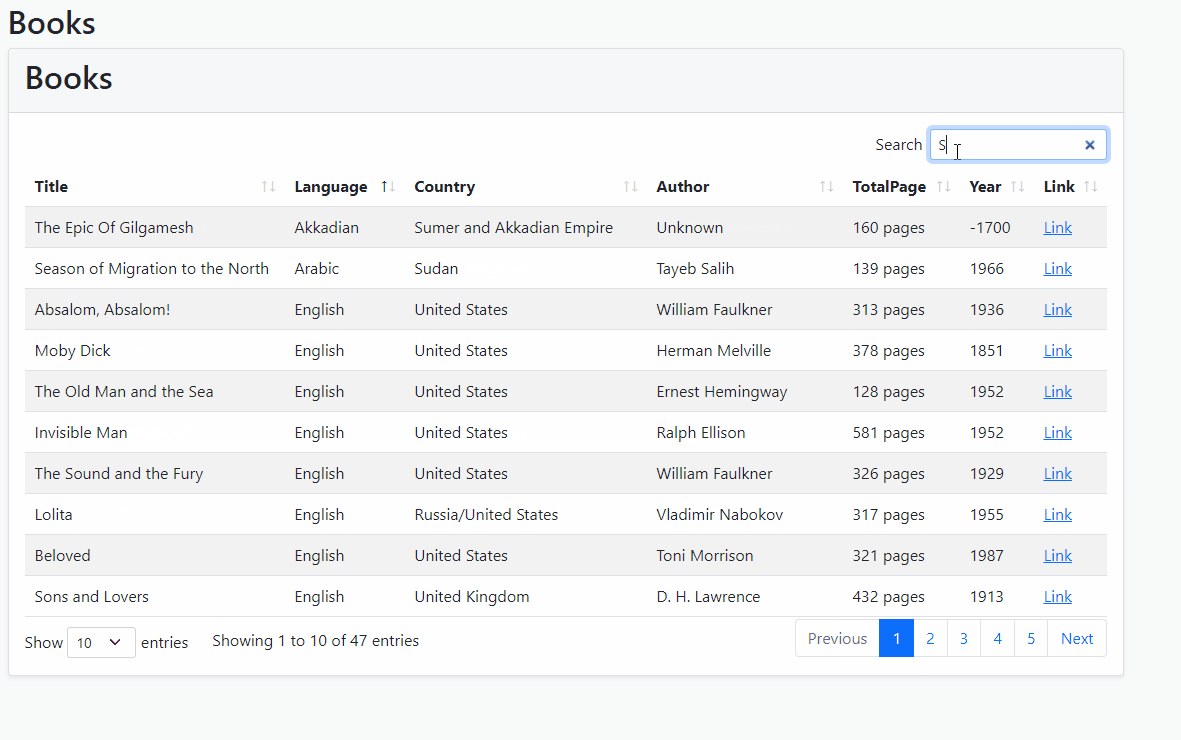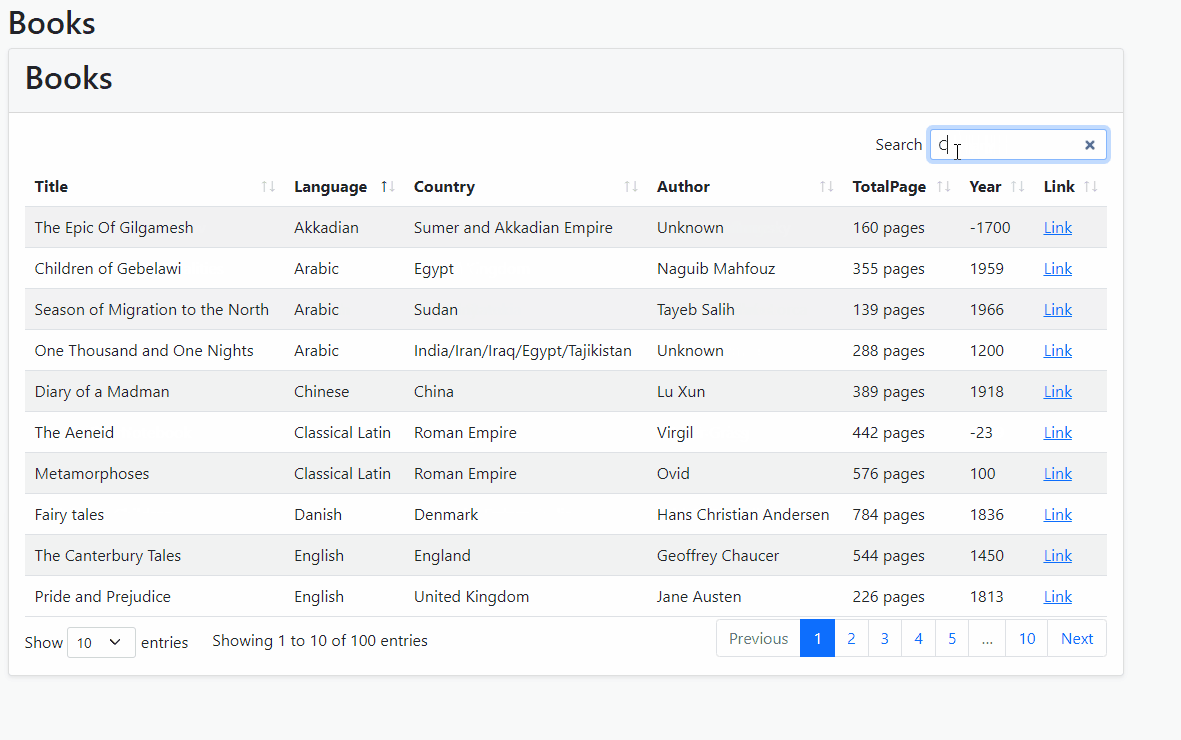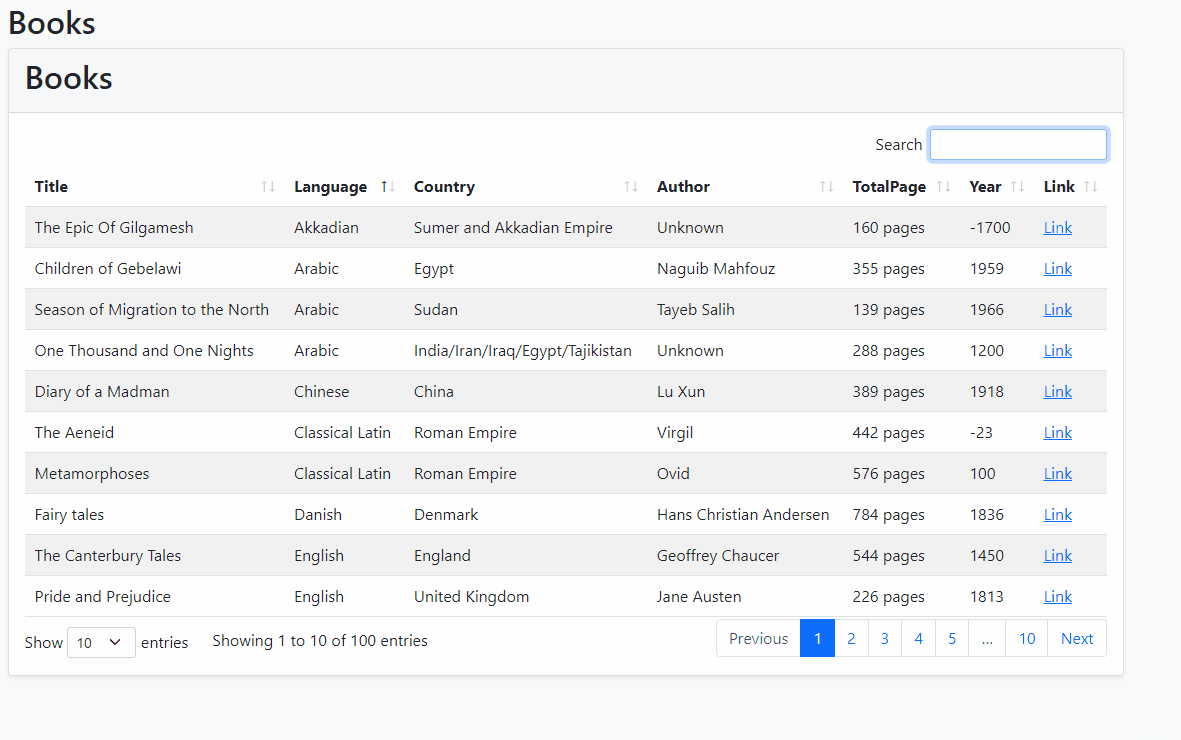
Filtering Specific Properties
AutoFilterer supports some different features like Filtering with Range. Let's filter TotalPage and Year properties with range.
- Add following
TotalPageandYearproperties to BookGetListInput.
public class BookGetListInput : FilterBase, IPagedAndSortedResultRequest
{
// Configure 'Filter' property for built-in search boxes.
[CompareTo(
nameof(BookDto.Title),
nameof(BookDto.Language),
nameof(BookDto.Author),
nameof(BookDto.Country)
)]
[StringFilterOptions(StringFilterOption.Contains)]
public string Filter { get; set; }
public Range<int> TotalPage { get; set; } // <-- Add this one
public Range<int> Year { get; set; } // <-- and this
// IPagedAndSortedResultRequest implementation below.
public int SkipCount { get; set; }
public int MaxResultCount { get; set; }
public string Sorting { get; set; }
}
- Update Index.cshtml too
@page
@using Acme.BookStore.Localization
@using Acme.BookStore.Web.Pages.Books
@using Microsoft.Extensions.Localization
@model IndexModel
@inject IStringLocalizer<BookStoreResource> L
<h2>Books</h2>
@section scripts
{
<abp-script src="/Pages/Books/index.js" />
}
<abp-card>
<abp-card-header>
<h2>@L["Books"]</h2>
</abp-card-header>
<abp-card-body>
<div id="books-filter-wrapper">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-6">
<label class="form-label"> TotalPage </label>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-6">
<label class="form-label">Min</label>
<input id="TotalPageMin" type="number" class="form-control" />
</div>
<div class="col-6">
<label class="form-label">Max</label>
<input id="TotalPageMax" type="number" class="form-control" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-6">
<label class="form-label"> Year </label>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-6">
<label class="form-label">Min</label>
<input id="YearMin" type="number" class="form-control" />
</div>
<div class="col-6">
<label class="form-label">Max</label>
<input id="YearMax" type="number" class="form-control" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="mt-2">
<abp-table striped-rows="true" id="BooksTable"></abp-table>
</div>
</abp-card-body>
</abp-card>
- Update index.js file to send those parameters to API
$(function () {
var l = abp.localization.getResource('BookStore');
var getFilter = function () {
return {
totalPage: {
min: $('#TotalPageMin').val(),
max: $('#TotalPageMax').val()
},
year: {
min: $('#YearMin').val(),
max: $('#YearMax').val()
}
};
};
$("#books-filter-wrapper :input").on('input', function () {
dataTable.ajax.reload();
});
var dataTable = $('#BooksTable').DataTable(
abp.libs.datatables.normalizeConfiguration({
serverSide: true,
paging: true,
order: [[1, "asc"]],
searching: true,
scrollX: true,
ajax: abp.libs.datatables.createAjax(acme.bookStore.books.book.getList, getFilter),
columnDefs: [
{
title: l('Title'),
data: "title"
},
{
title: l('Language'),
data: "language",
},
{
title: l('Country'),
data: "country",
},
{
title: l('Author'),
data: "author"
},
{
title: l('TotalPage'),
data: "totalPage",
render: function (data) {
return data + ' pages'
}
},
{
title: l('Year'),
data: "year"
},
{
title: l('Link'),
data: "link",
render: function (data) {
return '<a href="' + data + '" target="_blank">Link</a>';
}
},
]
})
);
});
- Run the Application and see the result
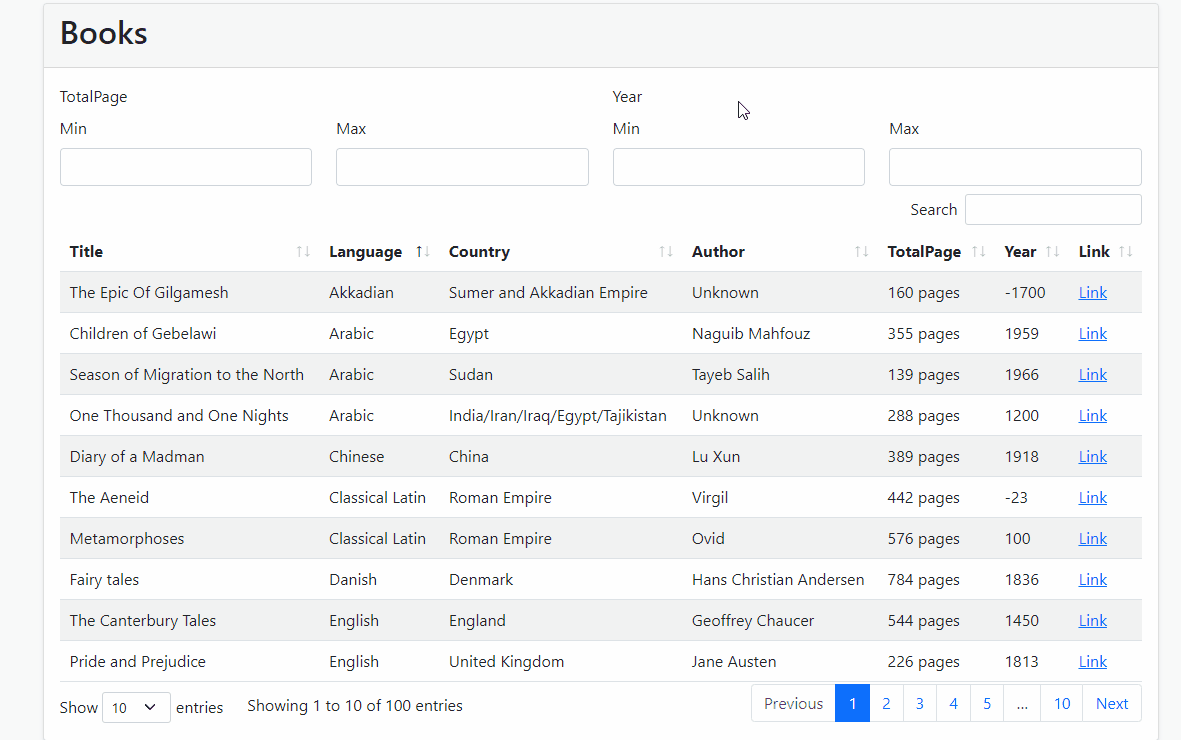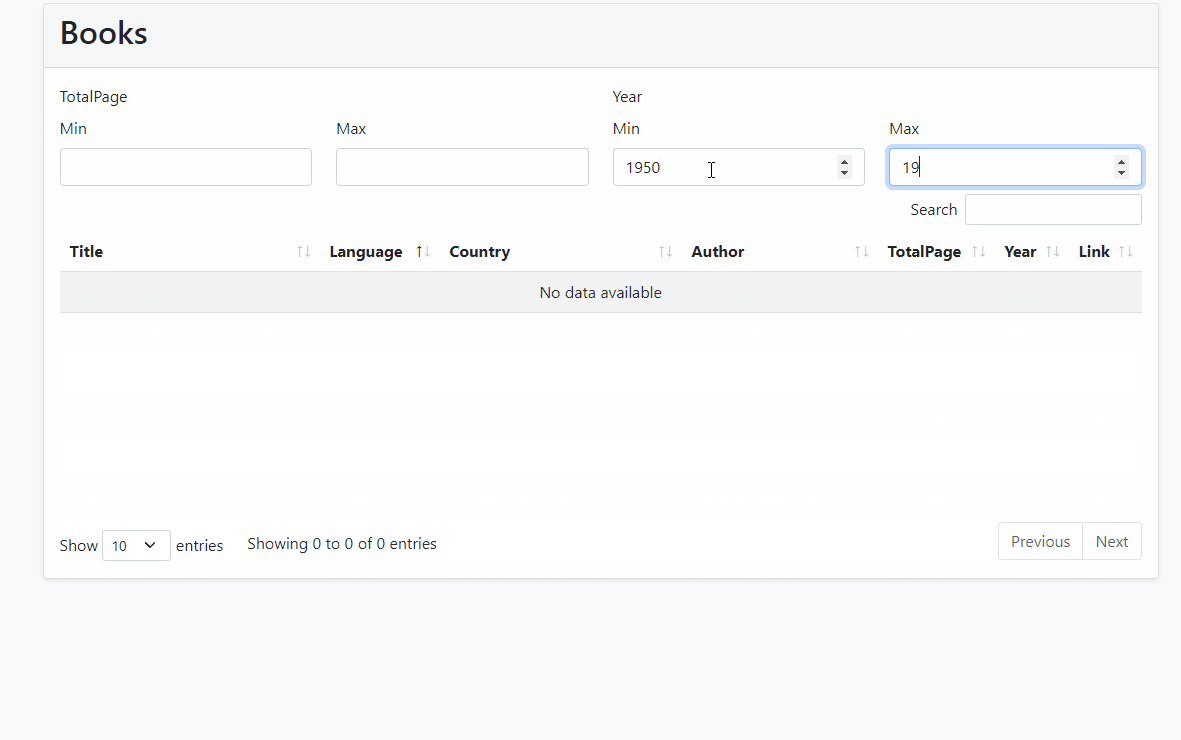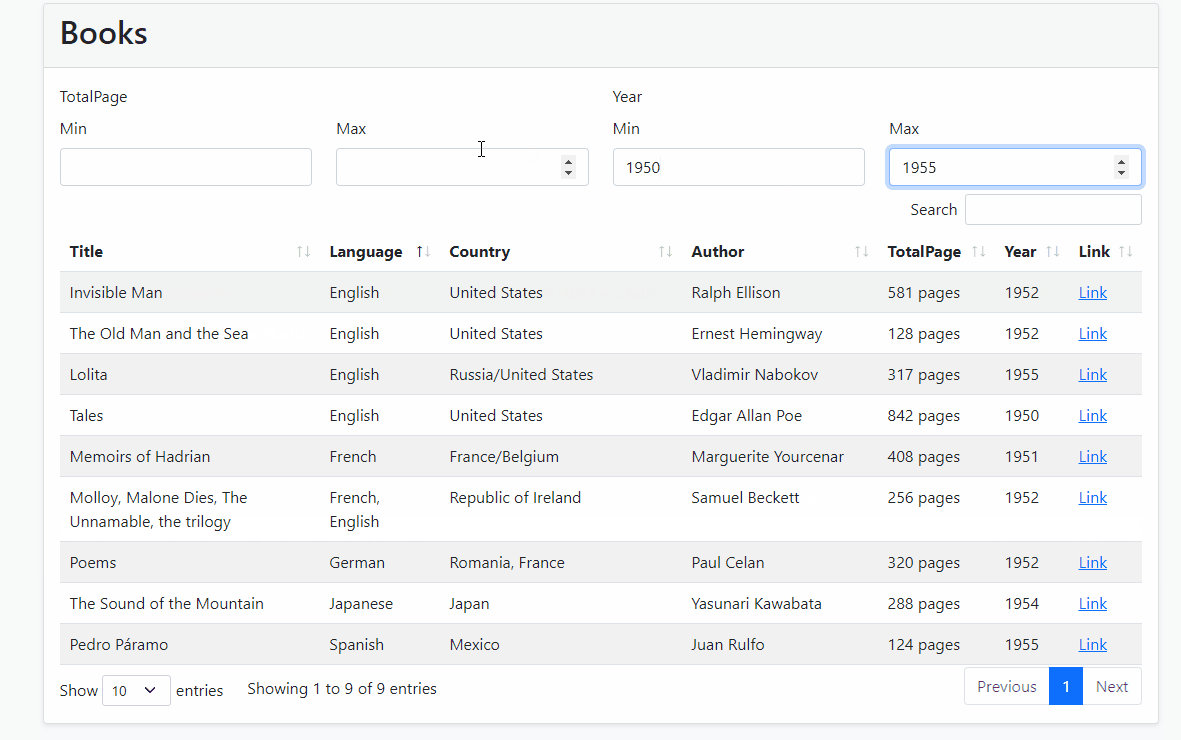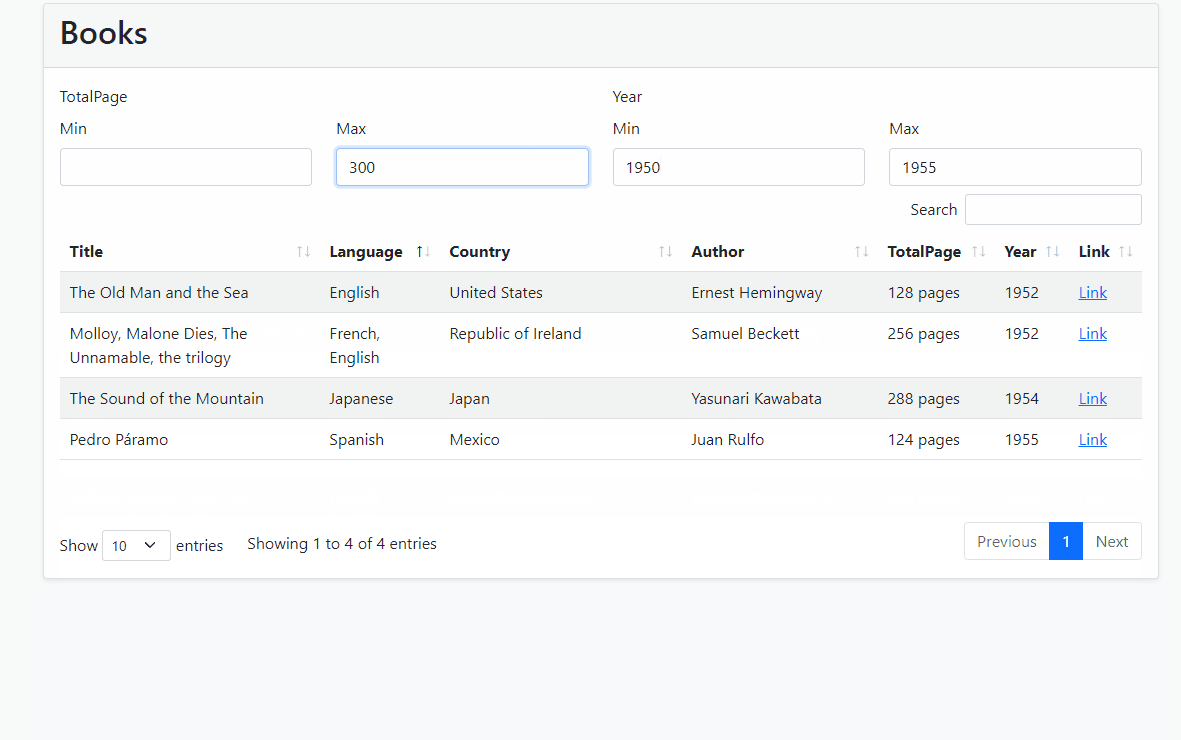
Source-Code
You can find final version of this example on github.
Discussion
There is a couple of questions that you can think about. In this "Discussion" section I'll try to answer them.
Is Defining Comparison in Dto ok?
As a first impression, I tough, it's not ok because Application.Contracts can be shipped to clients. It's true, definition of filter is in DTO, but the implementation is in Application layer. So if a developer who implements client-side, can see something like below.
public class BookGetListInput : FilterBase, IPagedAndSortedResultRequest
{
// Configure 'Filter' property for built-in search boxes.
[CompareTo(
nameof(BookDto.Title),
nameof(BookDto.Language),
nameof(BookDto.Author),
nameof(BookDto.Country)
)]
[StringFilterOptions(StringFilterOption.Contains)]
public string Filter { get; set; }
}
I think that's ok, because the developer'll understand what filtering does. It's kind of documentation with attributes.
Why didn't use Sorting & Pagination feature of AutoFilterer
ABP does those features well and UI frameworks(Razor Pages, Angular and Blazor) already implemented sorting and pagination with those existin parameters. Chaning cost is high because if you change, you'll need to implement them for each UI framework.




Comments
Engincan VESKE 121 weeks ago
Great library, thanks for sharing!